Shift Registers - Tutorial 6, Q&As
A Q&A tutorial to explore the use of the ez_SIPO8_lib in greater depth.
Components and supplies
Shift Register- Serial to Parallel
Resistor 220 ohm
Jumper wires (generic)
Arduino UNO
Breadboard (generic)
LED (generic)
Apps and platforms
Arduino IDE
Project description
Code
Sketch Example – Clock Chasing Second LEDs
c_cpp
Demonstration of use of ez_SIPO8_lib to simulate the chasing seconds of a clock face.
1// 2// Chasing LEDs - 3// This sketch illuminates a defined sequential array of LEDs connected to 4// SIPO output pins, at a specified frequency (milliseconds). 5// At the end of the LED sequence, the LEDs are reset and the 6// cycle repeated. 7// 8// The sketch can be configured for a SIPO array of any length, but this 9// example is configured to demonstrate the chasing LEDs of a clock dial. 10// In this instance the SIPO array length will be 64 output pins (8 x SIPOs) 11// but only the first 60 outputs will be used (0-59 seconds). The frequency 12// will be set to 1 second (1000 millisecs). 13// 14// This example uses absolute addressing of the defined SIPO array. 15// 16// Ron D Bentley, Stafford, UK 17// April 2021 18// 19// This example and code is in the public domain and 20// may be used without restriction and without warranty. 21// 22 23#include <ez_SIPO8_lib.h> 24 25#define Max_SIPOs 8 // 8 x SIPOs - provides 64 output pins 26#define Max_timers 1 // used to count 1 second elapsing 'beats' 27 28#define data_pin 8 29#define clock_pin 10 30#define latch_pin 9 31 32#define chase_length 60 // chasing seconds on a clock 33#define frequency 1000 // milli seconds - 1 second frequency 34 35// initiate the class for max SIPOs/timers required 36SIPO8 my_SIPOs(Max_SIPOs, Max_timers); 37 38int my_LEDs; // used to keep the SIPO bank id 39 40void setup() { 41 Serial.begin(9600); 42 // create a bank of 'Max_SIPOs' using create_bank function: 43 my_LEDs = my_SIPOs.create_bank(data_pin, clock_pin, latch_pin, Max_SIPOs); 44 if (my_LEDs == create_bank_failure) { 45 Serial.println(F("\ 46failed to create bank")); 47 Serial.flush(); 48 exit(0); 49 } 50 // start by setting all SIPO outputs to low (off) 51 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); 52 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); 53 // print the bank data for confirmation/inspection 54 my_SIPOs.print_SIPO_data(); 55} 56 57void loop() { 58 uint8_t next_pin = 0; 59 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // kick off the timer 60 do { 61 if (my_SIPOs.SIPO8_timer_elapsed(timer0, frequency) == elapsed) { 62 // 1 second time elapsed, so update next pin in the array 63 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // restart 1 second count for next cycle 64 if (next_pin == chase_length) { // wrap around 65 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); // clear all pins 66 next_pin = 0; 67 } else { 68 my_SIPOs.set_array_pin(next_pin, HIGH); // set absolute next_pin pin status 69 next_pin++; 70 } 71 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); // update physical SIPOs 72 } 73 } while (true); 74} 75
Sketch Example – Clock Chasing Second LEDs
c_cpp
Demonstration of use of ez_SIPO8_lib to simulate the chasing seconds of a clock face.
1// 2// Chasing LEDs - 3// This sketch illuminates a defined sequential array of LEDs connected to 4// SIPO output pins, at a specified frequency (milliseconds). 5// At the end of the LED sequence, the LEDs are reset and the 6// cycle repeated. 7// 8// The sketch can be configured for a SIPO array of any length, but this 9// example is configured to demonstrate the chasing LEDs of a clock dial. 10// In this instance the SIPO array length will be 64 output pins (8 x SIPOs) 11// but only the first 60 outputs will be used (0-59 seconds). The frequency 12// will be set to 1 second (1000 millisecs). 13// 14// This example uses absolute addressing of the defined SIPO array. 15// 16// Ron D Bentley, Stafford, UK 17// April 2021 18// 19// This example and code is in the public domain and 20// may be used without restriction and without warranty. 21// 22 23#include <ez_SIPO8_lib.h> 24 25#define Max_SIPOs 8 // 8 x SIPOs - provides 64 output pins 26#define Max_timers 1 // used to count 1 second elapsing 'beats' 27 28#define data_pin 8 29#define clock_pin 10 30#define latch_pin 9 31 32#define chase_length 60 // chasing seconds on a clock 33#define frequency 1000 // milli seconds - 1 second frequency 34 35// initiate the class for max SIPOs/timers required 36SIPO8 my_SIPOs(Max_SIPOs, Max_timers); 37 38int my_LEDs; // used to keep the SIPO bank id 39 40void setup() { 41 Serial.begin(9600); 42 // create a bank of 'Max_SIPOs' using create_bank function: 43 my_LEDs = my_SIPOs.create_bank(data_pin, clock_pin, latch_pin, Max_SIPOs); 44 if (my_LEDs == create_bank_failure) { 45 Serial.println(F("\ 46failed to create bank")); 47 Serial.flush(); 48 exit(0); 49 } 50 // start by setting all SIPO outputs to low (off) 51 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); 52 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); 53 // print the bank data for confirmation/inspection 54 my_SIPOs.print_SIPO_data(); 55} 56 57void loop() { 58 uint8_t next_pin = 0; 59 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // kick off the timer 60 do { 61 if (my_SIPOs.SIPO8_timer_elapsed(timer0, frequency) == elapsed) { 62 // 1 second time elapsed, so update next pin in the array 63 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // restart 1 second count for next cycle 64 if (next_pin == chase_length) { // wrap around 65 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); // clear all pins 66 next_pin = 0; 67 } else { 68 my_SIPOs.set_array_pin(next_pin, HIGH); // set absolute next_pin pin status 69 next_pin++; 70 } 71 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); // update physical SIPOs 72 } 73 } while (true); 74} 75
Sketch Example - Using an 8-bit SIPO to Display Switch Status
c_cpp
Displays status of six toggle switches (on or off) plus a heart beat monitor.
1/* 2 Ron D Bentley, Stafford, UK 3 April 2021 4 5 Example sketch 1 for Arduino Community story board 6 The sketch reads a number of toggle switches which are in one of two 7 states - on(HIGH) or off(LOW). 8 Each switch is mapped to a SIPO bank pin as follows: 9 switches 0-5 -> bank pins 0-5 10 bank pin 6 is not used 11 bank pin 7 is used as a sketch running indicator, 12 or 'heart beat' 13 14 Note that the switches are 'read' periodically sampled by a dummy 15 function using the SIPO8 timers feature. The code is non-blocking. 16 17 This example and code is in the public domain and 18 may be used without restriction and without warranty. 19 20*/ 21 22#include <ez_SIPO8_lib.h> 23 24#define Max_SIPOs 1 25#define Max_timers 1 26#define sample_time 500 // interval period between sampling sensors 27#define num_switches 6 // number of sensors requiring testing/reading in each cycle 28 29// initiate the class for max SIPOs/timers required 30SIPO8 my_SIPOs(Max_SIPOs, Max_timers); 31 32uint8_t bank_id; 33 34// dummy read switch function - returns a random staus for given switch 35// number, based on switch's current status 36bool read_switch_status(uint8_t Switch) { 37 randomSeed(analogRead(A0)*analogRead(A2)); // keep changing seed 38 if (random(0, 4) == 0)return !my_SIPOs.read_bank_pin(bank_id, Switch); 39 return my_SIPOs.read_bank_pin(bank_id, Switch); 40} 41 42void setup() { 43 Serial.begin(9600); 44 // create 1 bank of Max_SIPOs 45 // params are data pin, clock pin anf latch pin, number SIPOs 46 bank_id = my_SIPOs.create_bank(8, 10, 9, Max_SIPOs); 47 if (bank_id == create_bank_failure) { 48 Serial.println(F("failed to create bank")); 49 Serial.flush(); 50 exit(0); 51 } 52 my_SIPOs.print_SIPO_data(); // report on global SIPO8 params 53} 54// Scan all defined switches and set their respective bank pin status, LOW/HIGH. 55// Switches/bank pins layout: 56// Switch associated bank pins run from 0 to num_switches-1, inclusive (5) and 57// are used to indicate respective switch status, 58// bank pin 6 is not used and bank pin 7 is used to provide 59// a 'heart beat' to indicate that the sketch is running. 60void loop() { 61 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); // ensure we start with clear array pool/bank 62 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); 63 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // start the sample timer 64 do { 65 if (my_SIPOs.SIPO8_timer_elapsed(timer0, sample_time) == elapsed) { 66 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // reset/restart the timer 67 // read each switch and set its virtual SIPO pin in the bank 68 my_SIPOs.invert_bank_pin(bank_id, 7); // flash 'heart beat' 69 for (uint8_t Switch = 0; Switch < num_switches; Switch ++) { 70 my_SIPOs.set_bank_pin(bank_id, Switch, read_switch_status(Switch)); 71 } 72 my_SIPOs.xfer_bank(bank_id, MSBFIRST); // update the physical SIPO pins 73 } 74 } while (true); 75} 76
Sketch Example - Using an 8-bit SIPO to Display Switch Status
c_cpp
Displays status of six toggle switches (on or off) plus a heart beat monitor.
1/* 2 Ron D Bentley, Stafford, UK 3 April 2021 4 5 Example 6 sketch 1 for Arduino Community story board 7 The sketch reads a number of toggle 8 switches which are in one of two 9 states - on(HIGH) or off(LOW). 10 Each 11 switch is mapped to a SIPO bank pin as follows: 12 switches 0-5 -> bank pins 13 0-5 14 bank pin 6 is not used 15 bank pin 16 7 is used as a sketch running indicator, 17 or 'heart 18 beat' 19 20 Note that the switches are 'read' periodically sampled by a dummy 21 22 function using the SIPO8 timers feature. The code is non-blocking. 23 24 This 25 example and code is in the public domain and 26 may be used without restriction 27 and without warranty. 28 29*/ 30 31#include <ez_SIPO8_lib.h> 32 33#define 34 Max_SIPOs 1 35#define Max_timers 1 36#define sample_time 500 // 37 interval period between sampling sensors 38#define num_switches 6 // number 39 of sensors requiring testing/reading in each cycle 40 41// initiate the class 42 for max SIPOs/timers required 43SIPO8 my_SIPOs(Max_SIPOs, Max_timers); 44 45uint8_t 46 bank_id; 47 48// dummy read switch function - returns a random staus for given 49 switch 50// number, based on switch's current status 51bool read_switch_status(uint8_t 52 Switch) { 53 randomSeed(analogRead(A0)*analogRead(A2)); // keep changing seed 54 55 if (random(0, 4) == 0)return !my_SIPOs.read_bank_pin(bank_id, Switch); 56 return 57 my_SIPOs.read_bank_pin(bank_id, Switch); 58} 59 60void setup() { 61 Serial.begin(9600); 62 63 // create 1 bank of Max_SIPOs 64 // params are data pin, clock pin anf latch 65 pin, number SIPOs 66 bank_id = my_SIPOs.create_bank(8, 10, 9, Max_SIPOs); 67 68 if (bank_id == create_bank_failure) { 69 Serial.println(F("failed to create 70 bank")); 71 Serial.flush(); 72 exit(0); 73 } 74 my_SIPOs.print_SIPO_data(); 75 // report on global SIPO8 params 76} 77// Scan all defined switches and set 78 their respective bank pin status, LOW/HIGH. 79// Switches/bank pins layout: 80// 81 Switch associated bank pins run from 0 to num_switches-1, inclusive (5) and 82// 83 are used to indicate respective switch status, 84// bank pin 6 is not used and 85 bank pin 7 is used to provide 86// a 'heart beat' to indicate that the sketch is 87 running. 88void loop() { 89 my_SIPOs.set_all_array_pins(LOW); // ensure we start 90 with clear array pool/bank 91 my_SIPOs.xfer_array(MSBFIRST); 92 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); 93 // start the sample timer 94 do { 95 if (my_SIPOs.SIPO8_timer_elapsed(timer0, 96 sample_time) == elapsed) { 97 my_SIPOs.SIPO8_start_timer(timer0); // reset/restart 98 the timer 99 // read each switch and set its virtual SIPO pin in the bank 100 101 my_SIPOs.invert_bank_pin(bank_id, 7); // flash 'heart beat' 102 for (uint8_t 103 Switch = 0; Switch < num_switches; Switch ++) { 104 my_SIPOs.set_bank_pin(bank_id, 105 Switch, read_switch_status(Switch)); 106 } 107 my_SIPOs.xfer_bank(bank_id, 108 MSBFIRST); // update the physical SIPO pins 109 } 110 } while (true); 111} 112
Downloadable files
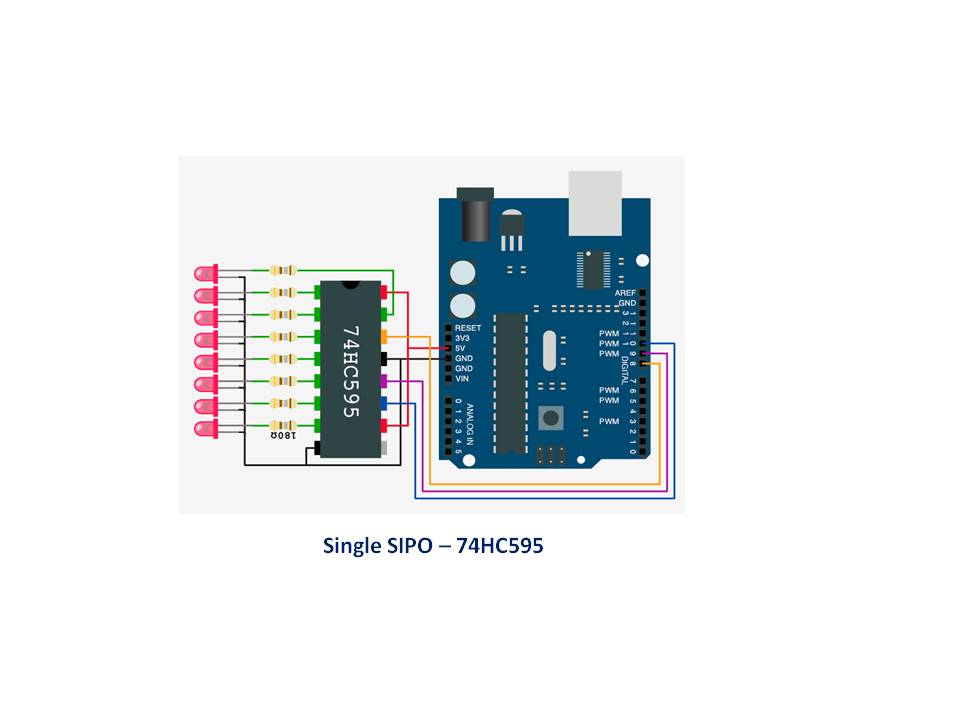
Single SIPO Shift Register, wiring diagram
Used throughout the tutorials
Single SIPO Shift Register, wiring diagram
Comments
Only logged in users can leave comments