Components and supplies
nRF24 Module (Generic)
Analog joystick (Generic)
LCD Screen 16 x 2
Project description
Code
Basic Joystick Code
arduino
Learn how to read the signals coming from the on board analog joysticks.
1/* Joystick_Basic Version 1.01 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 5/23/2019 4 * 5 * This code reads the value of each joystick 6 * axis using the Analog Read function. 7 * 8 * Each value for the joystick range should from 0-1023. 9 * The push-buttons should read 0 when pushed and 1 when not pushed. 10 * 11 */ 12 13void setup() { 14Serial.begin(115200); 15pinMode(5, OUTPUT); //Set the pins connected to the joystick button to an output 16pinMode(4, OUTPUT); 17digitalWrite(5, HIGH); //Set the pins to HIGH (5V). When the button is pressed it will pull the pin to ground (0V) 18digitalWrite(4, HIGH); 19} 20 21void loop() { 22 Serial.print("Joystick L: "); 23 Serial.print(analogRead(A2)); //Read the Joystick value 24 Serial.print("\ "); 25 Serial.print(analogRead(A3)); //Read the Joystick value 26 Serial.print("\ "); 27 Serial.print(digitalRead(4)); //Read the Button value 28 Serial.print("\ "); 29 30 Serial.print("Joystick R: "); //Read the Joystick value 31 Serial.print(analogRead(A0)); 32 Serial.print("\ "); 33 Serial.print(analogRead(A1)); //Read the Joystick value 34 Serial.print("\ "); 35 Serial.print(digitalRead(5)); //Read the Button value 36 Serial.print("\ "); 37 38 Serial.println(); 39 delay(10); 40} 41
Simple Receive
arduino
This is the code to receive wireless communication from the Arduino and the NRF24L01+ module.
1/* Simple Recieve Version 1.02 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 6/1/2019 4 * 5 * This code demonstrates how to use the NRF module to 6 * receive simple data from another NRF module. 7 * 8 * Note: This code requires another Arduino transmitting data 9 * from another NRF module using the Simple_Transmit Sketch 10 * 11 * Note: This code requires the use of the RF24 Library. 12 * You can easily download this library in the Arduino Library Manager. 13 */ 14 15#include <SPI.h> //Comes with Arduino IDE 16#include "RF24.h" //Download and Install (See above) 17 18#define CE_PIN 7 //The pins to be used for CE and CSN 19#define CSN_PIN 8 20 21RF24 radio(CE_PIN, CSN_PIN); 22 23byte addresses[][6] = {"1Node", "2Node"}; //These will be the names of the "Pipes" 24 25struct dataStruct { //this is the NRF data. Max of 32 bytes 26 int Xposition; //int = 2 bytes 27 int Yposition; //double = 4 bytes 28 bool switchOn; //boolean = 1 byte 29 30 int X2position; 31 int Y2position; 32 bool switch2On; 33} myData; //This can be accessed in the form: myData.Xposition etc. 34 35void setup() { 36 Serial.begin(115200); 37 radio.begin(); //Initialize the nRF24L01 Radio 38 radio.setChannel(108); //Above most WiFi frequencies (2.4Ghz + 0.108Ghz = 2.508Ghz) 39 radio.setDataRate(RF24_250KBPS); //Fast enough.. Better range 40 41 radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN); //This allows it to be used with only USB power. Use of RF24_PA_MAX requires battery connection 42 43 radio.openWritingPipe(addresses[1]); //Open a writing "Pipe" to send data out 44 radio.openReadingPipe(1, addresses[0]); //Open a reading "Pipe" to receive data 45 46 radio.startListening(); //Start listening for incoming data 47} 48 49 50void loop() { 51 52 if (radio.available()) { 53 radio.read( &myData, sizeof(myData) ); //If the NRF receives data on a Pipe read the data 54 Serial.print(myData.Xposition); Serial.print("\ "); //Print the data received 55 Serial.print(myData.Yposition); Serial.print("\ "); 56 Serial.print(myData.switchOn); Serial.print("\ "); 57 Serial.print(myData.X2position); Serial.print("\ "); 58 Serial.print(myData.Y2position); Serial.print("\ "); 59 Serial.print(myData.switch2On); Serial.print("\ "); 60 Serial.println(); 61 } 62 63} 64
Simple Transmit Code
arduino
This is the code to transmit Wireless Information with the Arduino and the NRF24L01+ module. This code uses the RF24 Library.
1/* Simple Transmit Version 1.02 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 6/1/2019 4 * 5 * This code demonstrates how to use the NRF module to 6 * transmit simple data to another NRF module. 7 * 8 * Note: This code requires another Arduino receiving data 9 * from another NRF module using the Simple_Recieve Sketch 10 * 11 * Note: This code requires the use of the RF24 Library. 12 * You can easily download this library in the Arduino Library Manager. 13 * 14 * Changes: The code now transmits the values of the joysticks rather 15 * than fixed values. 16 */ 17 18#include <SPI.h> //Comes with Arduino IDE 19#include "RF24.h" //Download and Install (See above) 20 21#define CE_PIN 7 //The pins to be used for CE and CSN 22#define CSN_PIN 8 23 24RF24 radio(CE_PIN, CSN_PIN); 25 26byte addresses[][6] = {"1Node", "2Node"}; //These will be the names of the "Pipes" 27 28struct dataStruct { //this is the NRF data. Max of 32 bytes 29 int Xposition; //int = 2 bytes 30 int Yposition; //double = 4 bytes 31 bool switchOn; //boolean = 1 byte 32 33 int X2position; 34 int Y2position; 35 bool switch2On; 36} myData; //This can be accessed in the form: myData.Xposition etc. 37 38 39void setup() { 40 Serial.begin(115200); 41 pinMode(5, OUTPUT); //Set up the Joysticks 42 pinMode(4, OUTPUT); 43 digitalWrite(5, HIGH); 44 digitalWrite(4, HIGH); 45 46 radio.begin(); //Initialize the nRF24L01 Radio 47 radio.setChannel(108); //Above most WiFi frequencies 48 radio.setDataRate(RF24_250KBPS); //Fast enough.. Better range 49 50 radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN); //This allows it to be used with only USB power. Use of RF24_PA_MAX requires battery connection 51 52 radio.openWritingPipe(addresses[0]); //Open a writing "Pipe" to send data out 53 radio.openReadingPipe(1, addresses[1]); //Open a reading "Pipe" to receive data 54 55 radio.stopListening(); //Stop Listening so we can start transmitting data 56 Serial.println("Set Up Complete"); 57} 58 59 60void loop() { 61 //This is the values that will be transmitted in the myData Struct 62 myData.Xposition = analogRead(A0); 63 myData.Yposition = analogRead(A1); 64 myData.switchOn = digitalRead(5); 65 66 myData.X2position = analogRead(A2); 67 myData.Y2position = analogRead(A3); 68 myData.switch2On = digitalRead(4); 69 70 radio.write(&myData, sizeof(myData), 1); //Transmit Data using the write command 71 Serial.println("Sent"); 72 delay(10); 73} 74
Basic Joystick Code
arduino
Learn how to read the signals coming from the on board analog joysticks.
1/* Joystick_Basic Version 1.01 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 5/23/2019 4 * 5 * This code reads the value of each joystick 6 * axis using the Analog Read function. 7 * 8 * Each value for the joystick range should from 0-1023. 9 * The push-buttons should read 0 when pushed and 1 when not pushed. 10 * 11 */ 12 13void setup() { 14Serial.begin(115200); 15pinMode(5, OUTPUT); //Set the pins connected to the joystick button to an output 16pinMode(4, OUTPUT); 17digitalWrite(5, HIGH); //Set the pins to HIGH (5V). When the button is pressed it will pull the pin to ground (0V) 18digitalWrite(4, HIGH); 19} 20 21void loop() { 22 Serial.print("Joystick L: "); 23 Serial.print(analogRead(A2)); //Read the Joystick value 24 Serial.print("\ "); 25 Serial.print(analogRead(A3)); //Read the Joystick value 26 Serial.print("\ "); 27 Serial.print(digitalRead(4)); //Read the Button value 28 Serial.print("\ "); 29 30 Serial.print("Joystick R: "); //Read the Joystick value 31 Serial.print(analogRead(A0)); 32 Serial.print("\ "); 33 Serial.print(analogRead(A1)); //Read the Joystick value 34 Serial.print("\ "); 35 Serial.print(digitalRead(5)); //Read the Button value 36 Serial.print("\ "); 37 38 Serial.println(); 39 delay(10); 40} 41
Voltage Sensor Code
arduino
Learn how to read battery voltage with an Arduino!
1/* Voltage Version 1.01 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 5/23/2019 4 * 5 * This code demostrates how to read the voltage 6 * applied to the Battery pins of the Pilot RC 7 * 8 * Note: This will display around 4.5 Volts when no battery is 9 * applied to the pins. This is because the pins are reading the 10 * voltage coming out of the 5V voltage regulator. 11 */ 12 13float vPow = 5.0; //constant for calculations (5V devices) 14float r1 = 49900; //Value of Resistor 1 15float r2 = 10000; //Value of Resistor 2 16float v, v2, vAvg, rcV, drV; 17int vNum; 18 19void setup() { 20 Serial.begin(115200); 21} 22 23 24void loop() { 25 v = (analogRead(A4) * vPow) / 1024.0; //Value of the voltage coming out of the voltage divider 26 v2 = v / (r2 / (r1 + r2)); //Actual voltage applied to the voltage divider (Battery Voltage) 27 vAvg += v2; //We want to average 100 readings of the battery voltage to achieve an accurate result 28 vNum++; 29 30 if (vNum == 100) { //Print the Voltage being read by the Pilot RC and reset the counters 31 rcV = vAvg/100; 32 Serial.print("Voltage: "); 33 Serial.println(rcV); 34 vNum=0; 35 vAvg=0; 36 } 37 38 delay(10); 39} 40
Simple Transmit Code
arduino
This is the code to transmit Wireless Information with the Arduino and the NRF24L01+ module. This code uses the RF24 Library.
1/* Simple Transmit Version 1.02 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 4 * Data: 6/1/2019 5 * 6 * This code demonstrates how to use the NRF module 7 to 8 * transmit simple data to another NRF module. 9 * 10 * Note: This 11 code requires another Arduino receiving data 12 * from another NRF module using 13 the Simple_Recieve Sketch 14 * 15 * Note: This code requires the use of the 16 RF24 Library. 17 * You can easily download this library in the Arduino Library 18 Manager. 19 * 20 * Changes: The code now transmits the values of the joysticks 21 rather 22 * than fixed values. 23 */ 24 25#include <SPI.h> //Comes with Arduino 26 IDE 27#include "RF24.h" //Download and Install (See above) 28 29#define CE_PIN 30 7 //The pins to be used for CE and CSN 31#define CSN_PIN 8 32 33RF24 radio(CE_PIN, 34 CSN_PIN); 35 36byte addresses[][6] = {"1Node", "2Node"}; //These will be the 37 names of the "Pipes" 38 39struct dataStruct { //this is the NRF data. 40 Max of 32 bytes 41 int Xposition; //int = 2 bytes 42 int Yposition; 43 //double = 4 bytes 44 bool switchOn; //boolean = 1 byte 45 46 47 int X2position; 48 int Y2position; 49 bool switch2On; 50} 51 myData; //This can be accessed in the form: myData.Xposition etc. 52 53 54void 55 setup() { 56 Serial.begin(115200); 57 pinMode(5, OUTPUT); //Set 58 up the Joysticks 59 pinMode(4, OUTPUT); 60 digitalWrite(5, HIGH); 61 digitalWrite(4, 62 HIGH); 63 64 radio.begin(); //Initialize the nRF24L01 Radio 65 66 radio.setChannel(108); //Above most WiFi frequencies 67 radio.setDataRate(RF24_250KBPS); 68 //Fast enough.. Better range 69 70 radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN); //This allows 71 it to be used with only USB power. Use of RF24_PA_MAX requires battery connection 72 73 74 radio.openWritingPipe(addresses[0]); //Open a writing "Pipe" to send data 75 out 76 radio.openReadingPipe(1, addresses[1]); //Open a reading "Pipe" to receive 77 data 78 79 radio.stopListening(); //Stop Listening so we can 80 start transmitting data 81 Serial.println("Set Up Complete"); 82} 83 84 85void 86 loop() { 87 //This is the values that will be transmitted in the myData Struct 88 89 myData.Xposition = analogRead(A0); 90 myData.Yposition = analogRead(A1); 91 92 myData.switchOn = digitalRead(5); 93 94 myData.X2position = analogRead(A2); 95 96 myData.Y2position = analogRead(A3); 97 myData.switch2On = digitalRead(4); 98 99 100 radio.write(&myData, sizeof(myData), 1); //Transmit Data using the write command 101 102 Serial.println("Sent"); 103 delay(10); 104} 105
Voltage Sensor Code
arduino
Learn how to read battery voltage with an Arduino!
1/* Voltage Version 1.01 2 * Author: Schindler Electronics 3 * Data: 4 5/23/2019 5 * 6 * This code demostrates how to read the voltage 7 * applied 8 to the Battery pins of the Pilot RC 9 * 10 * Note: This will display around 11 4.5 Volts when no battery is 12 * applied to the pins. This is because the pins 13 are reading the 14 * voltage coming out of the 5V voltage regulator. 15 */ 16 17float 18 vPow = 5.0; //constant for calculations (5V devices) 19float r1 = 49900; //Value 20 of Resistor 1 21float r2 = 10000; //Value of Resistor 2 22float v, v2, vAvg, 23 rcV, drV; 24int vNum; 25 26void setup() { 27 Serial.begin(115200); 28} 29 30 31void 32 loop() { 33 v = (analogRead(A4) * vPow) / 1024.0; //Value of the voltage coming 34 out of the voltage divider 35 v2 = v / (r2 / (r1 + r2)); //Actual 36 voltage applied to the voltage divider (Battery Voltage) 37 vAvg += v2; //We 38 want to average 100 readings of the battery voltage to achieve an accurate result 39 40 vNum++; 41 42 if (vNum == 100) { //Print the Voltage being 43 read by the Pilot RC and reset the counters 44 rcV = vAvg/100; 45 Serial.print("Voltage: 46 "); 47 Serial.println(rcV); 48 vNum=0; 49 vAvg=0; 50 } 51 52 53 delay(10); 54} 55
Downloadable files
schematic_9aA1vmIpMI.jpg
schematic_9aA1vmIpMI.jpg
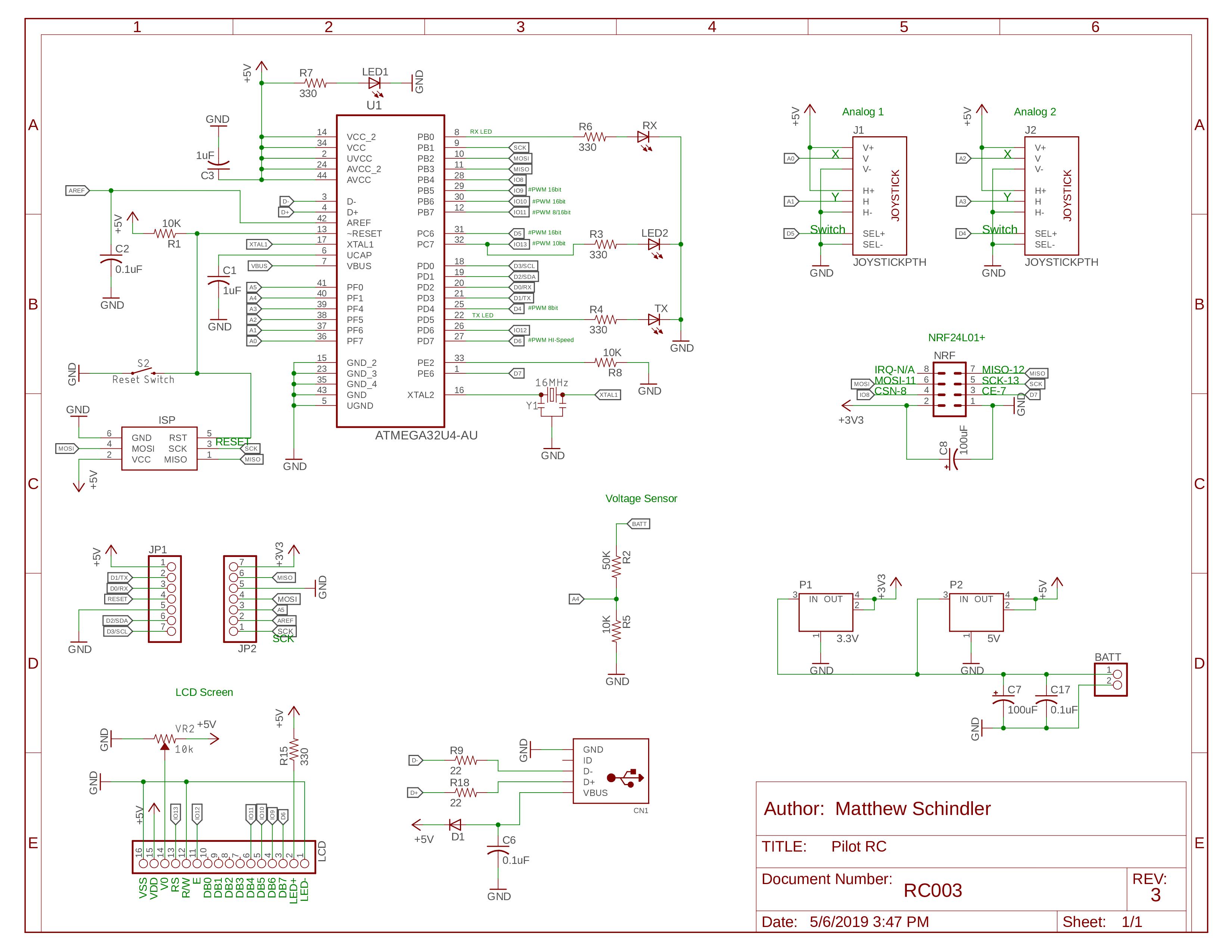
schematic_9aA1vmIpMI.jpg
schematic_9aA1vmIpMI.jpg

Documentation
3D Printed Case
The 3D printable case for the Pilot RC!
3D Printed Case
3D Printed Case
The 3D printable case for the Pilot RC!
3D Printed Case
Comments
Only logged in users can leave comments