Components and supplies
zmpt 101b
MapleTree Mini - STM32duino STM32F103RB Compatible with Leaf Maple
SCT-013
NodeMCU ESP8266 Breakout Board
Apps and platforms
Blynk
Project description
Code
Code that is compiled into the NodeMCU
arduino
Code that is compiled into the NodeMCU, Basically it makes a serial communication with the STM32 and sends all that info to Blynk app.
1#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial 2#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> 3#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h> 4#include <ArduinoJson.h> 5#include <SoftwareSerial.h> 6SoftwareSerial s(3,1); 7 8//TX RX como serial. 9//LEMBRAR DE LIGAR OS TERRAS JUNTOS. 10 11// You should get Auth Token in the Blynk App. 12// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon). 13char auth[] = "EBzOKyeWePRCay5fP8tY-eMnQVQmY0x5"; 14 15// Your WiFi credentials. 16// Set password to "" for open networks. 17char ssid[] = "motorolaone"; 18char pass[] = "batata12"; 19WidgetLCD lcd(V10); 20int value; 21String PotFase1; 22String PotFase2; 23String PotFase3; 24int Pot1; 25int Pot2; 26int Pot3; 27int i1; 28int i2; 29int i3; 30int v1; 31int v2; 32int v3; 33int FP1; 34int FP2; 35int FP3; 36int Energia; 37float Preco; 38int PotAux; 39char serialRead; 40BlynkTimer timer; 41 42// This function sends Arduino's up time every second to Virtual Pin (5). 43// In the app, Widget's reading frequency should be set to PUSH. This means 44// that you define how often to send data to Blynk App. 45 46 47void myTimerEvent() 48{ 49 50 51 Blynk.virtualWrite(V1,Pot1); 52 delay(50); 53 Blynk.virtualWrite(V2,Pot2); 54 delay(50); 55 Blynk.virtualWrite(V3,Pot3); 56 delay(50); 57 Blynk.virtualWrite(V4,v1); 58 delay(50); 59 Blynk.virtualWrite(V5,i1); 60 delay(50); 61 Blynk.virtualWrite(V6,v2); 62 delay(50); 63 Blynk.virtualWrite(V7,i2); 64 delay(50); 65 Blynk.virtualWrite(V8,v3); 66 delay(80); 67 Blynk.virtualWrite(V9,i3); 68 delay(50); 69 Blynk.virtualWrite(V10,FP1); 70 delay(50); 71 Blynk.virtualWrite(V11,FP2); 72 delay(50); 73 Blynk.virtualWrite(V12,FP3); 74 delay(50); 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 // You can send any value at any time. 82 // Please don't send more that 10 values per second. 83} 84 85void setup() 86{ 87 // Debug console 88 Serial.begin(9600); 89 s.begin(9600); 90 while (!Serial) continue; 91 Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass); 92 timer.setInterval(2000L, myTimerEvent); 93} 94 95void loop() 96{ 97 s.write("s"); 98 if (s.available()>0) 99 { 100 serialRead = s.read(); 101 if (serialRead == 'A'){ 102 s.write("s"); 103 if (s.available()>0){ 104 PotAux=s.read(); 105 if(PotAux>=0){ 106 Pot1=PotAux;}} 107 s.write("s"); 108 if (s.available()>0){ 109 PotAux=s.read(); 110 if(PotAux>=0){ 111 Pot1=100*PotAux+Pot1;}} 112 } 113 if (serialRead == 'B'){ 114 s.write("s"); 115 if (s.available()>0){ 116 PotAux=s.read(); 117 if(PotAux>=0){ 118 Pot2=PotAux;}} 119 s.write("s"); 120 if (s.available()>0){ 121 PotAux=s.read(); 122 if(PotAux>=0){ 123 Pot2=100*PotAux+Pot2;}} 124 } 125 126 if (serialRead == 'C'){ 127 s.write("s"); 128 if (s.available()>0){ 129 PotAux=s.read(); 130 if(PotAux>=0){ 131 Pot3=PotAux;}} 132 s.write("s"); 133 if (s.available()>0){ 134 PotAux=s.read(); 135 if(PotAux>=0){ 136 Pot3=100*PotAux+Pot3;}} 137 } 138 139 if (serialRead == 'D'){ 140 s.write("s"); 141 PotAux=s.read(); 142 if(PotAux>=0){ 143 i1=PotAux;} 144 } 145 146 if (serialRead == 'E'){ 147 s.write("s"); 148 PotAux=s.read(); 149 if(PotAux>=0){ 150 v1=PotAux;} 151 } 152 153 if (serialRead == 'F'){ 154 s.write("s"); 155 PotAux=s.read(); 156 if(PotAux>=0){ 157 i2=PotAux;} 158 } 159 160 if (serialRead == 'G'){ 161 s.write("s"); 162 PotAux=s.read(); 163 if(PotAux>=0){ 164 v2=PotAux;} 165 } 166 167 168 if (serialRead == 'H'){ 169 s.write("s"); 170 PotAux=s.read(); 171 if(PotAux>=0){ 172 i3=PotAux;} 173 } 174 175 if (serialRead == 'I'){ 176 s.write("s"); 177 PotAux=s.read(); 178 if(PotAux>=0){ 179 v3=PotAux;} 180 } 181 182 if (serialRead == 'J'){ 183 s.write("s"); 184 PotAux=s.read(); 185 if(PotAux>=0){ 186 Energia=PotAux;} 187 } 188 189 if (serialRead == 'K'){ 190 s.write("s"); 191 PotAux=s.read(); 192 if(PotAux>=0){ 193 FP1=PotAux;} 194 } 195 196 if (serialRead == 'L'){ 197 s.write("s"); 198 PotAux=s.read(); 199 if(PotAux>=0){ 200 FP2=PotAux;} 201 } 202 203 if (serialRead == 'M'){ 204 s.write("s"); 205 PotAux=s.read(); 206 if(PotAux>=0){ 207 FP3=PotAux;} 208 } 209 210 } 211 212 213 214 Blynk.run(); 215 timer.run(); // Initiates BlynkTimer 216}
Code that is compiled into the NodeMCU
arduino
Code that is compiled into the NodeMCU, Basically it makes a serial communication with the STM32 and sends all that info to Blynk app.
1#define BLYNK_PRINT Serial 2#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> 3#include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h> 4#include 5 <ArduinoJson.h> 6#include <SoftwareSerial.h> 7SoftwareSerial s(3,1); 8 9//TX 10 RX como serial. 11//LEMBRAR DE LIGAR OS TERRAS JUNTOS. 12 13// You should get 14 Auth Token in the Blynk App. 15// Go to the Project Settings (nut icon). 16char 17 auth[] = "EBzOKyeWePRCay5fP8tY-eMnQVQmY0x5"; 18 19// Your WiFi credentials. 20// 21 Set password to "" for open networks. 22char ssid[] = "motorolaone"; 23char 24 pass[] = "batata12"; 25WidgetLCD lcd(V10); 26int value; 27String PotFase1; 28String 29 PotFase2; 30String PotFase3; 31int Pot1; 32int Pot2; 33int Pot3; 34int i1; 35int 36 i2; 37int i3; 38int v1; 39int v2; 40int v3; 41int FP1; 42int FP2; 43int FP3; 44int 45 Energia; 46float Preco; 47int PotAux; 48char serialRead; 49BlynkTimer timer; 50 51// 52 This function sends Arduino's up time every second to Virtual Pin (5). 53// In 54 the app, Widget's reading frequency should be set to PUSH. This means 55// that 56 you define how often to send data to Blynk App. 57 58 59void myTimerEvent() 60{ 61 62 63 64 Blynk.virtualWrite(V1,Pot1); 65 delay(50); 66 Blynk.virtualWrite(V2,Pot2); 67 68 delay(50); 69 Blynk.virtualWrite(V3,Pot3); 70 delay(50); 71 Blynk.virtualWrite(V4,v1); 72 73 delay(50); 74 Blynk.virtualWrite(V5,i1); 75 delay(50); 76 Blynk.virtualWrite(V6,v2); 77 78 delay(50); 79 Blynk.virtualWrite(V7,i2); 80 delay(50); 81 Blynk.virtualWrite(V8,v3); 82 83 delay(80); 84 Blynk.virtualWrite(V9,i3); 85 delay(50); 86 Blynk.virtualWrite(V10,FP1); 87 88 delay(50); 89 Blynk.virtualWrite(V11,FP2); 90 delay(50); 91 Blynk.virtualWrite(V12,FP3); 92 93 delay(50); 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 // You can send any value at 101 any time. 102 // Please don't send more that 10 values per second. 103} 104 105void 106 setup() 107{ 108 // Debug console 109 Serial.begin(9600); 110 s.begin(9600); 111 112 while (!Serial) continue; 113 Blynk.begin(auth, ssid, pass); 114 timer.setInterval(2000L, 115 myTimerEvent); 116} 117 118void loop() 119{ 120 s.write("s"); 121 if (s.available()>0) 122 123 { 124 serialRead = s.read(); 125 if (serialRead == 'A'){ 126 s.write("s"); 127 128 if (s.available()>0){ 129 PotAux=s.read(); 130 if(PotAux>=0){ 131 Pot1=PotAux;}} 132 133 s.write("s"); 134 if (s.available()>0){ 135 PotAux=s.read(); 136 137 if(PotAux>=0){ 138 Pot1=100*PotAux+Pot1;}} 139 } 140 if (serialRead 141 == 'B'){ 142 s.write("s"); 143 if (s.available()>0){ 144 PotAux=s.read(); 145 146 if(PotAux>=0){ 147 Pot2=PotAux;}} 148 s.write("s"); 149 if 150 (s.available()>0){ 151 PotAux=s.read(); 152 if(PotAux>=0){ 153 Pot2=100*PotAux+Pot2;}} 154 155 } 156 157 if (serialRead == 'C'){ 158 s.write("s"); 159 if (s.available()>0){ 160 161 PotAux=s.read(); 162 if(PotAux>=0){ 163 Pot3=PotAux;}} 164 s.write("s"); 165 166 if (s.available()>0){ 167 PotAux=s.read(); 168 if(PotAux>=0){ 169 170 Pot3=100*PotAux+Pot3;}} 171 } 172 173 if (serialRead == 'D'){ 174 s.write("s"); 175 176 PotAux=s.read(); 177 if(PotAux>=0){ 178 i1=PotAux;} 179 } 180 181 182 if (serialRead == 'E'){ 183 s.write("s"); 184 PotAux=s.read(); 185 186 if(PotAux>=0){ 187 v1=PotAux;} 188 } 189 190 if (serialRead == 'F'){ 191 192 s.write("s"); 193 PotAux=s.read(); 194 if(PotAux>=0){ 195 i2=PotAux;} 196 197 } 198 199 if (serialRead == 'G'){ 200 s.write("s"); 201 PotAux=s.read(); 202 203 if(PotAux>=0){ 204 v2=PotAux;} 205 } 206 207 208 if (serialRead == 209 'H'){ 210 s.write("s"); 211 PotAux=s.read(); 212 if(PotAux>=0){ 213 214 i3=PotAux;} 215 } 216 217 if (serialRead == 'I'){ 218 s.write("s"); 219 220 PotAux=s.read(); 221 if(PotAux>=0){ 222 v3=PotAux;} 223 } 224 225 226 if (serialRead == 'J'){ 227 s.write("s"); 228 PotAux=s.read(); 229 230 if(PotAux>=0){ 231 Energia=PotAux;} 232 } 233 234 if (serialRead == 235 'K'){ 236 s.write("s"); 237 PotAux=s.read(); 238 if(PotAux>=0){ 239 240 FP1=PotAux;} 241 } 242 243 if (serialRead == 'L'){ 244 s.write("s"); 245 246 PotAux=s.read(); 247 if(PotAux>=0){ 248 FP2=PotAux;} 249 } 250 251 252 if (serialRead == 'M'){ 253 s.write("s"); 254 PotAux=s.read(); 255 256 if(PotAux>=0){ 257 FP3=PotAux;} 258 } 259 260 } 261 262 263 264 265 Blynk.run(); 266 timer.run(); // Initiates BlynkTimer 267}
Code that is compiled into the STM32f103
arduino
Code that is compiled into the STM32f103. All functions used in metering are implemented in this code
1#include <LiquidCrystal.h> 2 3 4const int rs = PB11, en = PB10, d4 = PA7, d5 = PA6, d6 = PC13, d7 = PC14; //mention the pin names to with LCD is connected to 5LiquidCrystal lcd(rs, en, d4, d5, d6, d7); //Initialize the LCD 6float Tensao; 7float Corrente; 8float Potencia; 9float Energia=0; 10float EnergiaAux; 11int T_sample; 12int Fase; 13const int PinTensao1=PB0; 14const int PinCorrente1=PA0; 15const int PinTensao2=PB1; 16const int PinCorrente2=PA1; 17const int PinTensao3=PA5; 18const int PinCorrente3=PA4; 19const int PinbotaoMode=PA11; 20const int PinbotaoZerar=PA12; 21//EnergyMonitor SCT1; 22//EnergyMonitor SCT2; 23//EnergyMonitor SCT3; 24int botaoMode=0; 25int estado1; 26int estado2; 27int estadoAux; 28int ZeroTP1; 29int ZeroTP2; 30int ZeroTP3; 31int ZeroTC1; 32int ZeroTC2; 33int ZeroTC3; 34int PotFase11; 35int PotFase21; 36int PotFase31; 37int PotFase12; 38int PotFase22; 39int PotFase32; 40int Potfin; 41int i1; 42int i2; 43int i3; 44int v1; 45int v2; 46int v3; 47int FP1; 48int FP2; 49int FP3; 50float FPaux; 51unsigned long Tempo1; 52unsigned long Tempo2; 53unsigned long Tempo3; 54 55void setup() { 56 57 Serial1.begin(9600); 58 lcd.begin(16, 2);//We are using a 16*2 LCD 59 analogReadResolution(12); 60 pinMode(PinTensao1, INPUT); 61 pinMode(PinCorrente1, INPUT); 62 pinMode(PinTensao2, INPUT); 63 pinMode(PinCorrente2, INPUT); 64 pinMode(PinTensao3, INPUT); 65 pinMode(PinCorrente3, INPUT); 66 pinMode(PinbotaoMode, INPUT); 67 pinMode(PinbotaoZerar, INPUT); 68 Fase=0; 69 T_sample=10; 70 estado1=LOW; 71 estado2=HIGH; 72 estadoAux=0; 73 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); 74 lcd.print("Aguarde a config"); 75 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); 76 lcd.print("A Vazio"); 77 delay(10000); 78 79 80 ZeroTP1=ZeroADC(PinTensao1); 81 ZeroTP2=ZeroADC(PinTensao2); 82 ZeroTP3=ZeroADC(PinTensao3); 83 ZeroTC1=ZeroADC(PinCorrente1)-5; 84 ZeroTC2=ZeroADC(PinCorrente2); 85 ZeroTC3=ZeroADC(PinCorrente3); 86 //ZeroTP1=100; 87 //ZeroTP2=0; 88 //ZeroTP3=0; 89 //ZeroTC1=100; 90 //ZeroTC2=100; 91 //ZeroTC3=100; 92 lcd.clear(); 93 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); 94 delay(1500); 95 lcd.print("Configurado!"); 96 delay(1500); 97 98} 99 100 101void loop() { 102 Tempo1=micros(); 103 if(Fase==0){ 104 105 //Bloco para teste de valor maximo digital, tempo para realização do analog read. 106 //lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 107 //Tempo1=micros(); 108 //Tensao = analogRead(PinTensao1); 109 //Tempo2=micros(); 110 //lcd.print(Tensao); 111 //lcd.setCursor(0, 1); 112 //Tempo3=Tempo2-Tempo1; 113 //lcd.print(Tempo2-Tempo1); 114 115 Potencia=LCDMode(botaoMode,Fase,PinCorrente1,PinTensao1,Energia,ZeroTP1,ZeroTC1); 116 PotFase11=(int)Potencia/100; 117 PotFase12=Potencia - 100*PotFase11; 118 i1=arredonda(RMS(52.5,PinCorrente1,1000,ZeroTC1)); 119 v1=arredonda(RMS(403,PinTensao1,1000,ZeroTP1)); 120 FPaux=FatordePotencia(PinTensao1,PinCorrente1,ZeroTP1,ZeroTC1,403,52.5); 121 FP1=(int)100*abs(FPaux); 122 123 124 } 125 if(Fase==1){ 126 Potencia=LCDMode(botaoMode,Fase,PinCorrente2,PinTensao2,Energia,ZeroTP2,ZeroTC2); 127 PotFase21=(int)Potencia/100; 128 PotFase22=Potencia - 100*PotFase21; 129 i2=arredonda(RMS(52.5,PinCorrente2,1000,ZeroTC2)); 130 v2=arredonda(RMS(403,PinTensao2,1000,ZeroTP2)); 131 FPaux=(int) 100*FatordePotencia(PinTensao2,PinCorrente2,ZeroTP2,ZeroTC2,403,52.5); 132 FP2=(int)100*abs(FPaux); 133 } 134 if(Fase==2){ 135 Potencia=LCDMode(botaoMode,Fase,PinCorrente3,PinTensao3,Energia,ZeroTP3,ZeroTC3); 136 PotFase31=(int)Potencia/100; 137 PotFase32=Potencia - 100*PotFase31; 138 i3=arredonda(RMS(52.5,PinCorrente3,1000,ZeroTC3)); 139 v3=arredonda(RMS(403,PinTensao3,1000,ZeroTP3)); 140 FPaux=(int) 100*FatordePotencia(PinTensao3,PinCorrente3,ZeroTP3,ZeroTC3,403,52.5); 141 FP3=(int)100*abs(FPaux); 142 } 143 144 145 146 147 if(Serial1.available()>0) // comunicação serial com o ESP8266 148 //Cada letra tem um feature sendo enviado 149 { 150 151 Serial1.write('A'); 152 if(Serial1.available()>0) 153 { 154 Serial1.write(PotFase12); 155 if(Serial1.available()>0){ 156 Serial1.write(PotFase11); 157 } 158 } 159 160 Serial1.write('B'); 161 if(Serial1.available()>0) 162 { 163 Serial1.write(PotFase22); 164 if(Serial1.available()>0){ 165 Serial1.write(PotFase21); 166 } 167 } 168 169 170 Serial1.write('C'); 171 if(Serial1.available()>0) 172 { 173 Serial1.write(PotFase32); 174 if(Serial1.available()>0){ 175 Serial1.write(PotFase31); 176 } 177 } 178 179 Serial1.write('D'); 180 if(Serial1.available()>0) 181 { 182 Serial1.write(i1);} 183 184 Serial1.write('E'); 185 if(Serial1.available()>0) 186 { 187 Serial1.write(v1);} 188 189 190 Serial1.write('F'); 191 if(Serial1.available()>0) 192 { 193 Serial1.write(i2);} 194 195 Serial1.write('G'); 196 if(Serial1.available()>0) 197 { 198 Serial1.write(v2);} 199 200 201 Serial1.write('H'); 202 if(Serial1.available()>0) 203 { 204 Serial1.write(i3);} 205 206 207 Serial1.write('I'); 208 if(Serial1.available()>0) 209 { 210 Serial1.write(v3);} 211 212 Serial1.write('J'); 213 if(Serial1.available()>0) 214 { 215 Serial1.write(arredonda(Energia));} 216 217 Serial1.write('K'); 218 if(Serial1.available()>0) 219 { 220 Serial1.write(FP1);} 221 222 Serial1.write('L'); 223 if(Serial1.available()>0) 224 { 225 Serial1.write(FP2);} 226 227 Serial1.write('M'); 228 if(Serial1.available()>0) 229 { 230 Serial1.write(FP3);} 231 232 233 } 234 235 236 237 238 estado1=digitalRead(PinbotaoMode);// Lógica para mudar a variavel botaomode de acordo com o apertar do botao. isso mudara o que o LCD enxergará 239 if((estado1==LOW) and (estadoAux==HIGH)){ 240 241 if(botaoMode<4){ 242 botaoMode++; 243 lcd.clear(); 244 } 245 else{ 246 botaoMode=0; 247 lcd.clear(); 248 } 249 estadoAux=estado1; 250 } 251 else{ 252 estadoAux=estado1; 253 } 254 255 256 estado2=digitalRead(PinbotaoZerar); //Lógica para zerar energia. 257 if(estado2==HIGH){ 258 Energia=0; 259 } 260 261 262 263 264 265 if(Fase<2){ // Mudar de fase a cada loop 266 Fase++; 267 } 268 else { 269 Fase=0; 270 } 271 272 delay(200); 273 Tempo2=micros(); 274 275 EnergiaAux=(Tempo2-Tempo1)/10000; 276 EnergiaAux=EnergiaAux/100; 277 EnergiaAux=Potencia*3*EnergiaAux/1000; 278 EnergiaAux=EnergiaAux/3600;// Não esta em kw hora 279 Energia=EnergiaAux+Energia; 280 281 282 283} 284 285 286float RMS(float constante, const int pinEntrada, int samples,int zero){ 287 288 int i; // Calculo de RMS discreto para uma só variável. Usar constante para fazer a tranformação na medição elétrica 289 float Valor; 290 float Result=0; 291 float zeroaux=0; 292 for(i=0;i<samples;i++){ 293 Valor=analogRead(pinEntrada); 294 Valor=Valor-zero; 295 Valor=3.3*(Valor)/4096; 296 Result=Valor*Valor+Result; 297 } 298 Result=Result/samples; 299 Result=sqrt(Result); 300 Result=constante*Result; // para o sensor de corrente = (3.3/4096)*(2000/Resistencia) 301 return Result; 302} 303float RMS_simultaneo(float constante1,float constante2,const int pinEntrada1,const int pinEntrada2,int samples,int mode,int zero1, int zero2){ 304 305 int i; // Calculo de RMS discreto ; constante1 e constante2 para transformação da tensao e corrente em valores reais 306 float Valor1; 307 float Valor2; 308 float Result1=0; 309 float Result2=0; 310 float Resultfinal; 311 unsigned long Tempo1; 312 unsigned long Tempo2; 313 314 Tempo1=micros(); 315 for(i=0;i<samples;i++){ 316 317 Valor1 = analogRead(pinEntrada1); 318 Valor1=Valor1-zero1; 319 Valor1=3.3*(Valor1)/4096;// usar constantes aqui, para transformar em valores reais. 320 Valor2 = analogRead(pinEntrada2); 321 Valor2=Valor2-zero2; 322 Valor2=3.3*(Valor2)/4096;// mudar de acordo com o ADC 323 Result1=Valor1*Valor1+Result1; 324 Result2=Valor2*Valor2+Result2; 325 } 326 Result1=Result1/samples; 327 Result2=Result2/samples; 328 Result1=sqrt(Result1); 329 Result2=sqrt(Result2); 330 Result1=constante1*Result1; //para o sensor de corrente = (3.3/4096)*(2000/Resistencia) 331 Result2=constante2*Result2;// para o de tensão é impirico 332 Resultfinal=Result1*Result2; 333 Tempo2=micros(); 334 335 if(mode==0){ 336 Resultfinal=Resultfinal*(Tempo2-Tempo1)/1000000; // definir mode=0 para medir a energia. Converter para unidade de tempo certa 337 } 338 339 340 return Resultfinal; 341} 342 343float FatordePotencia(const int pinEntrada1,const int pinEntrada2,int Zero1, int Zero2,float constante1, float constante2){ // Falta definir quem é um e quem é dois para saber se a corrente esta atrasada ou adiantada 344 345 float Patv=0; 346 float Preact; 347 int samples=1480; 348 float FatPot; 349 int i; 350 float Valor1; 351 float Valor2; 352 for(i=0;i<samples;i++){ 353 Valor1 = analogRead(pinEntrada1); 354 Valor2 = analogRead(pinEntrada2); 355 Valor1=Valor1-Zero1; 356 Valor1=constante1*3.3*(Valor1)/4096; 357 Valor2=Valor2-Zero2; 358 Valor2=constante2*3.3*(Valor2)/4096;// mudar de acordo com o ADC 359 Patv=Valor1*Valor2+Patv; 360 } 361 Patv=Patv/samples; 362 Preact=RMS_simultaneo(403,52.5,pinEntrada1,pinEntrada2,1480,1,Zero1,Zero2); 363 FatPot=Patv/Preact; 364 //Patv=Patv/(Tempo2-Tempo1) 365 // FatPot=(Tempo1-Tempo2)/46.2; //(46.2 é o quanto demora para a onda de 60hz andar um grau) resultado aqui é o numero de graus 366 // FatPot=FatPot*(2*3.14159/360); // Passando pra radiano. 367 //FatPot=cos(FatPot); //fator de potencia 368 369 return FatPot; 370 371} 372 373int arredonda(float number) 374{ 375 return (number >= 0) ? (int)(number + 0.5) : (int)(number - 0.5); 376} 377 378int ZeroADC(const int A){ 379 int i; 380 int sum=0; 381 int aux; 382 for(i=0;i<40;i++){ 383 aux=analogRead(A); 384 sum=aux+sum; 385 } 386 sum=sum/40; 387 return sum; 388} 389 390float LCDMode(int botao,int fase, const int pinI,const int pinV,float E,int zeroV,int zeroI) { 391 int a; 392 int b; 393 float preco=0.5; 394 float precofinal; 395 float V; 396 float I; 397 float P; 398 float FP; 399 P=RMS_simultaneo(403,52.5,pinV,pinI,1000,1,zeroV,zeroI); //Calculo da potencia. 400 401 402 403 if(fase==0){ // setar cursor do LCD de acordo com a fase 404 a=9; 405 b=0; 406 } 407 if(fase==1){ 408 a=2; 409 b=1; 410 } 411 if(fase==2){ 412 a=9; 413 b=1; 414 } 415 416 417 if(botao==0){ //Tensão 418 // Printando a tela do usuario. 419 420 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 421 lcd.print("U(Volt)A:"); //Print 422 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //elemento 1x2 423 lcd.print("B:"); //Print 424 lcd.setCursor(7, 1); 425 lcd.print("C:"); 426 427 V=RMS(403,pinV,1480,zeroV); 428 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 429 lcd.print(" "); 430 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 431 lcd.print(V,1); 432 } 433 if(botao==1){ //Corrente 434 435 436 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 437 lcd.print("I(Amp) A:"); //Print 438 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //elemento 1x2 439 lcd.print("B:"); //Print 440 lcd.setCursor(7, 1); 441 lcd.print("C:"); 442 I=RMS(52.5,pinI,1480,zeroI); 443 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 444 lcd.print(" "); 445 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 446 lcd.print(I,1); 447 } 448 if(botao==2){ // Potencia instantanea 449 450 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 451 lcd.print("Pot(W) A:"); //Print 452 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //elemento 1x2 453 lcd.print("B:"); //Print 454 lcd.setCursor(7, 1); 455 lcd.print("C:"); 456 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 457 lcd.print(" "); 458 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 459 lcd.print(P,0); 460 } 461 if(botao==3){ // Energia 462 463 464 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 465 lcd.print("E(kWh):"); //Print 466 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //elemento 1x2 467 lcd.print("Preco:"); //Print 468 lcd.setCursor(6, 1); 469 precofinal=preco*E; 470 lcd.print(precofinal,2); 471 472 lcd.setCursor(9,0); 473 lcd.print(E,2); 474 475 } 476 if(botao==4){ // Fator de potência 477 478 479 lcd.setCursor(0, 0); //elemento 1x1 480 lcd.print("FP A:"); //Print 481 lcd.setCursor(0, 1); //elemento 1x2 482 lcd.print("B:"); //Print 483 lcd.setCursor(7, 1); 484 lcd.print("C:"); 485 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 486 FP=FatordePotencia(pinV,pinI,zeroV,zeroI,403,52.5); 487 lcd.setCursor(a,b); 488 lcd.print(FP,2); 489 } 490 491 return P; 492 493}
Downloadable files
Schematic
The schematic including all the hardware od the power metter.
Schematic
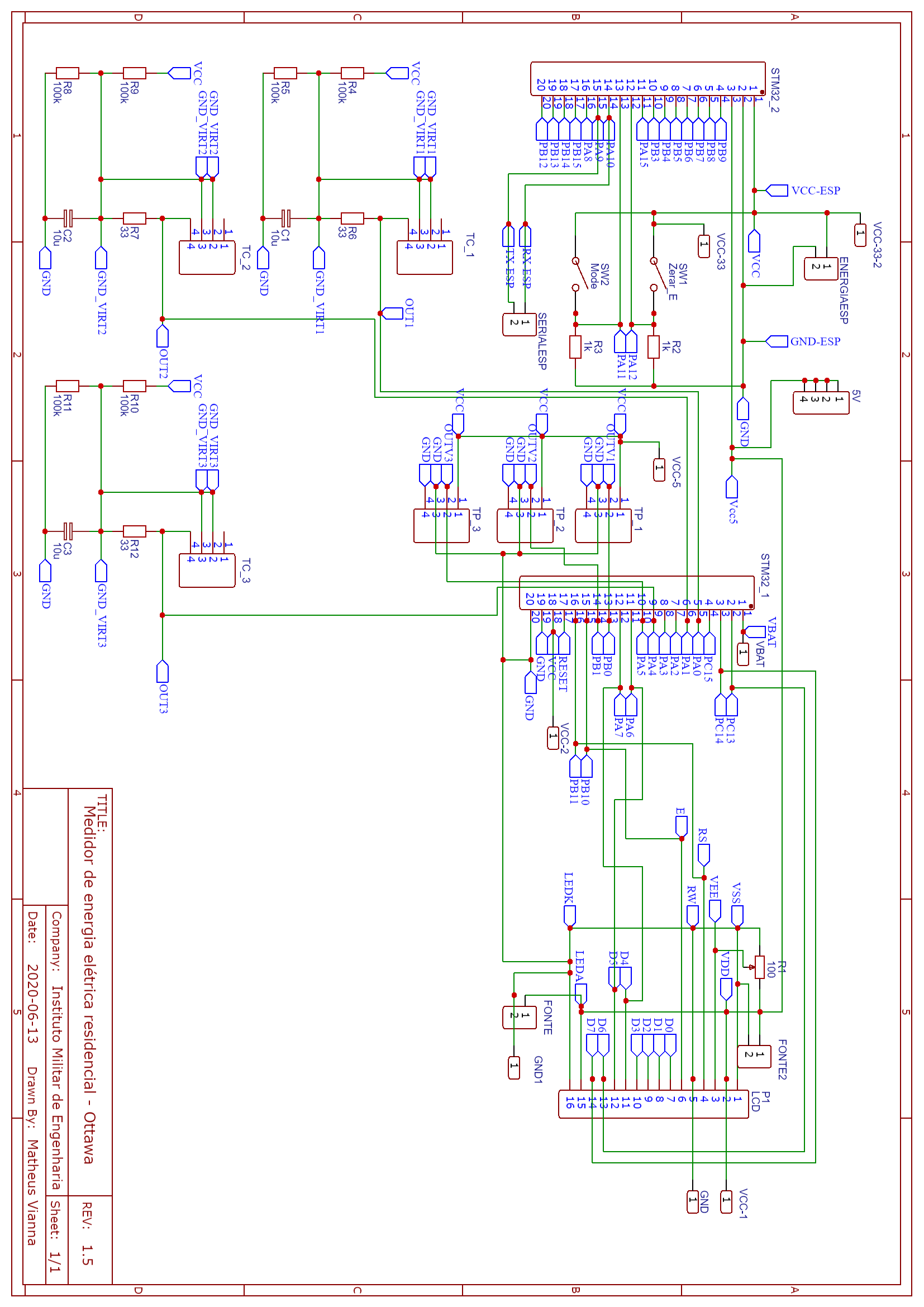
Schematic
The schematic including all the hardware od the power metter.
Schematic

Comments
Only logged in users can leave comments