Components and supplies
1
Arduino Uno Rev3
11
Jumper wires (generic)
1
Solderless Breadboard Full Size
10
Resistor 330 ohm
Project description
Code
Flash_Bright_Beginner_code
arduino
There are two circuits to see and the code shows how everything works.
1/* Flash BRIGHT = Larsen scanner/Knight Rider easy-learner coding. 2 By Neil Doherty 09/2019 3 First, the Arduino Editor does not load these notes onto a board, 4it only loads the operating code. 5 Pins are where you push jumper wires into. 6*/ 7 8int LED3 = 3; // Each Arduino pin has a number or name. 9int LED4 = 4; // Here,a value is assigned to the pins 10int LED5 = 5; // numbered 3 to 12, using int (integer). 11int LED6 = 6; // A jumper-wire connects each Arduino pin 12int LED7 = 7; // to the positive/long leg of an LED 13int LED8 = 8; // (L-ight E-mitting D-iode) on a 'breadboard'. 14int LED9 = 9; // As it's name implies, an actual breadboard 15int LED10 = 10; // was first used to tap pins into and wires 16int LED11 = 11; // strung between, making connections. 17int LED12 = 12; 18 19const int DELAY = 50; // const int uses less memory than int. 20 // For this circuit all of them could use 21 // const int, but it illustrates both uses. 22 // The main difference is that with int, 23 // you can change the value inside the loop 24 // function which you will come to learn can 25 // be very useful, whereas const int cannot 26 // be changed. 27void setup() { 28 29 30 pinMode(LED3, OUTPUT); // pinMode is a command to the Arduino 31 pinMode(LED4, OUTPUT); // to apply what is in the brackets. 32 pinMode(LED5, OUTPUT); // < in this case, (LED5,set to transmit) 33 pinMode(LED6, OUTPUT); // And so on for the others. 34 pinMode(LED7, OUTPUT); // INPUT only applies to certain pins when 35 pinMode(LED8, OUTPUT); // used. 36 pinMode(LED9, OUTPUT); 37 pinMode(LED10, OUTPUT); 38 pinMode(LED11, OUTPUT); 39 pinMode(LED12, OUTPUT); 40 41 42 digitalWrite(12, LOW); // These commands switch all the LEDs 43 digitalWrite(11, LOW); // to no power out. LOW meaning OFF 44 digitalWrite(10, LOW); // HIGH meaning ON 45 digitalWrite(9, LOW); // These lines make sure ALL LEDs are 46 digitalWrite(8, LOW); // off to begin with. 47 digitalWrite(7, LOW); 48 digitalWrite(6, LOW); 49 digitalWrite(5, LOW); 50 digitalWrite(4, LOW); 51 digitalWrite(3, LOW); 52 53} 54 55void loop() { 56 //Forward 57 digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // Switch LED attached to pin 12 on 58 delay(DELAY); // allowing the LED to light up HIGH 59 digitalWrite(12, LOW); // for a period of DELAY = 50 60 delay(DELAY); // microseconds = 50m, where 1000m is 1 second. 61 digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // Then it is switched LOW for the next 50m 62 delay(DELAY); 63 digitalWrite(11, LOW); // This section lights the LEDs in one direction 64 delay(DELAY); 65 digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // digitalwrite just says 'let there be light' 66 delay(DELAY); // well, only for the relevant LED, that is. 67 digitalWrite(10, LOW); // It instructs the Arduino to make the power 68 delay(DELAY); // to the pin ON/HIGH or OFF/LOW. 69 digitalWrite(9, HIGH); 70 delay(DELAY); 71 digitalWrite(9, LOW); 72 delay(DELAY); 73 digitalWrite(8, HIGH); 74 delay(DELAY); 75 digitalWrite(8, LOW); 76 delay(DELAY); 77 digitalWrite(7, HIGH); 78 delay(DELAY); 79 digitalWrite(7, LOW); 80 delay(DELAY); 81 digitalWrite(6, HIGH); 82 delay(DELAY); 83 digitalWrite(6, LOW); 84 delay(DELAY); 85 digitalWrite(5, HIGH); 86 delay(DELAY); 87 digitalWrite(5, LOW); 88 delay(DELAY); 89 digitalWrite(4, HIGH); 90 delay(DELAY); 91 digitalWrite(4, LOW); 92 delay(DELAY); 93 digitalWrite(3, HIGH); 94 delay(DELAY); 95 digitalWrite(3, LOW); 96 delay(DELAY); 97 98 // NOW Reverse 99 100 digitalWrite(4, LOW); // This section makes the LEDs light up 101 delay(DELAY); // in the other direction. 102 digitalWrite(5, HIGH); 103 delay(DELAY); 104 digitalWrite(5, LOW); // You might notice, and wonder, why this 105 delay(DELAY); // section has neither 3 nor 12 pins repeated. 106 delay(DELAY); // That is because it would cause the two end 107 digitalWrite(6, LOW); // LEDs to double-flash, which would look strange 108 delay(DELAY); // To be sure, add them in, upload again and 109 digitalWrite(7, HIGH); // see it happen. 110 delay(DELAY); 111 digitalWrite(7, LOW); // Experiment by changing 112 delay(DELAY); 113 digitalWrite(8, HIGH); 114 delay(DELAY); 115 digitalWrite(8, LOW); 116 delay(DELAY); 117 digitalWrite(9, HIGH); 118 delay(DELAY); 119 digitalWrite(9, LOW); 120 delay(DELAY); 121 digitalWrite(10, HIGH); 122 delay(DELAY); 123 digitalWrite(10, LOW); 124 delay(DELAY); 125 digitalWrite(11, HIGH); 126 delay(DELAY); 127 digitalWrite(11, LOW); 128 delay(DELAY); 129 130}
Downloadable files
Comparison Knight Rider circuits
Super-beginner programming.
Comparison Knight Rider circuits
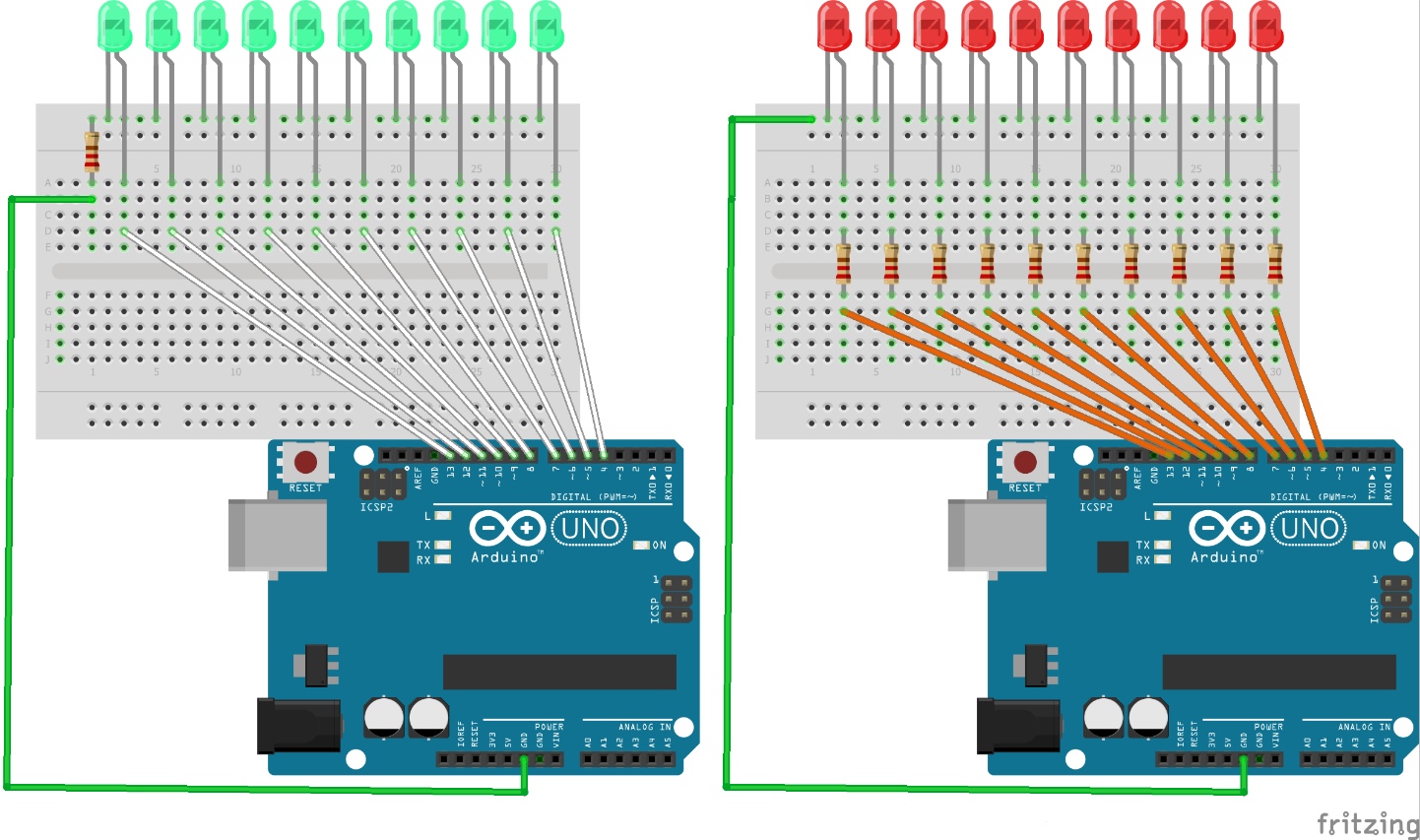
Comparison Knight Rider circuits
Super-beginner programming.
Comparison Knight Rider circuits

Comments
Only logged in users can leave comments